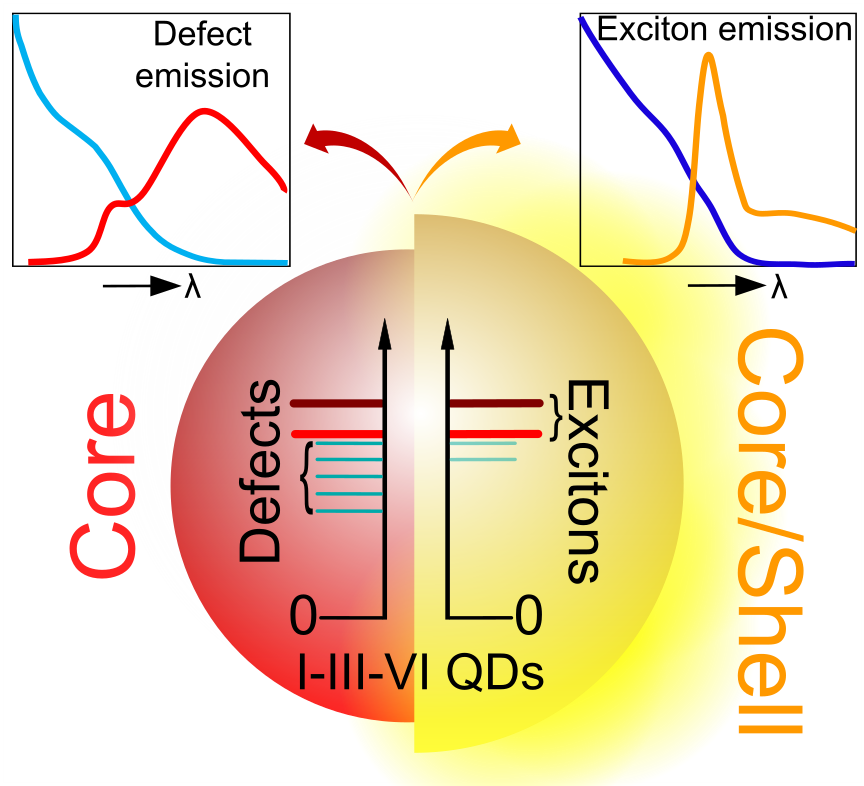
In situ spectroscopy
In-situ spectroscopy is a power tool to “look” into the reaction that drives many chemical and physical aspects of quantum dots. Here, we combine in situ absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy, with a time resolution down to milliseconds, to study a wide variety of chemical and physical process of quantum dots. This includes their growth dynamics during the synthesis, anion exchange reactions used to tune their composition as well as surface treatments with metal salts and ligands. This overall gives us a unique insight in what drives these physical and chemical processes, which in turn is used to optimize the photophysical properties of our colloidal quantum dots.
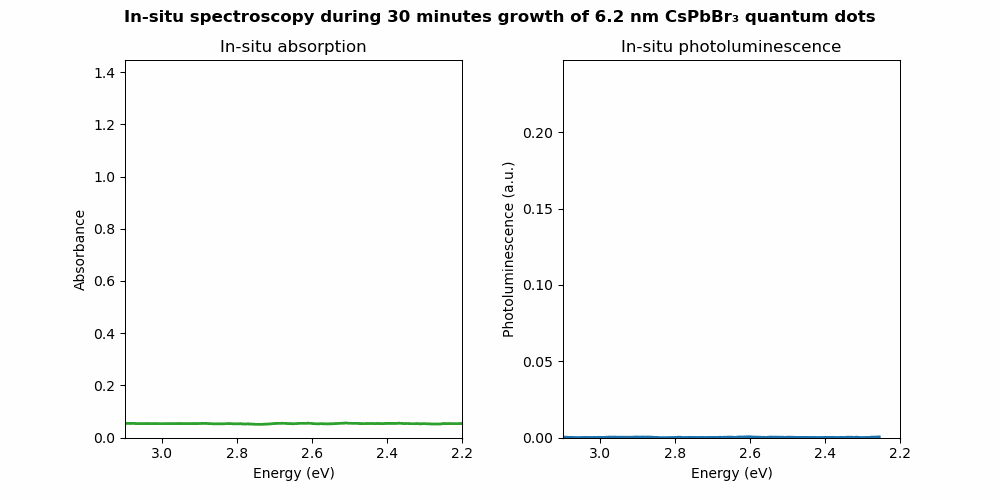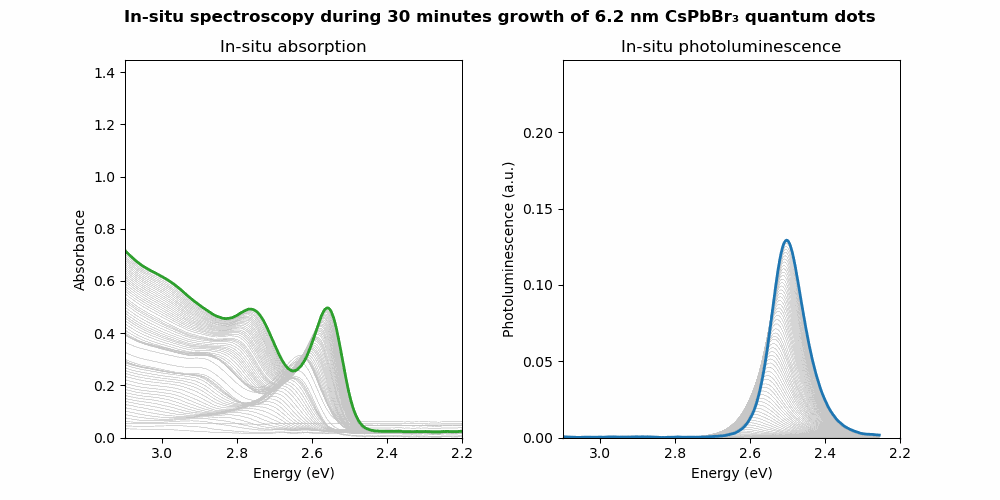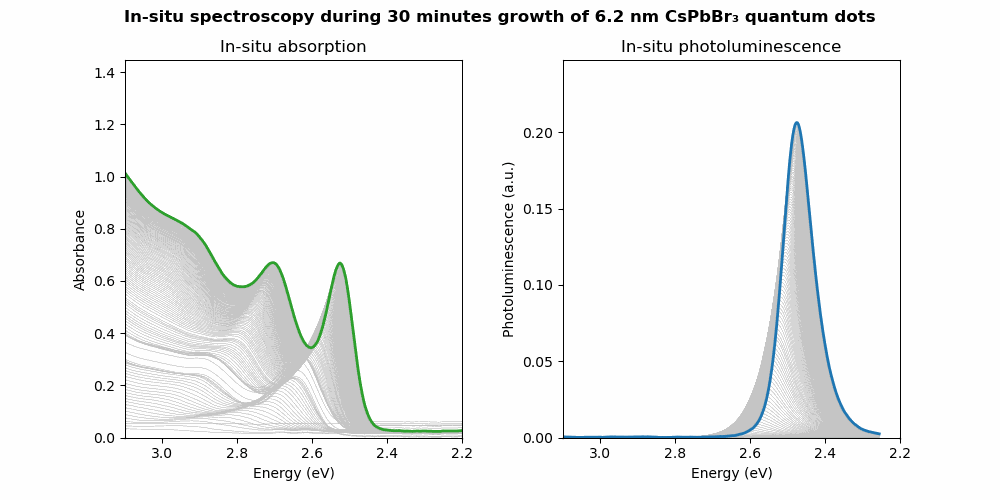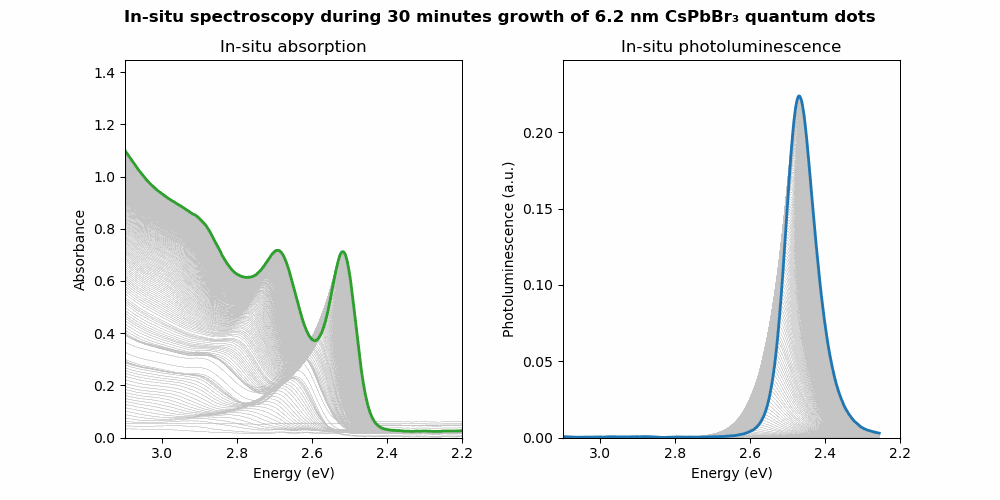
Selected works on this topic:
- Quantum Dot Metal Salt Interactions Unraveled by the Sphere of Action Model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 14395-14403 (2023)
- Spheroidal Cesium Lead Chloride–Bromide Quantum Dots and a Fast Determination of Their Size and Halide Content Nano Lett. Nano Lett. 22, 8168–8173 (2022)
- Controlling the nucleation and growth kinetics of lead halide perovskite quantum dots. Science 377, 1406-1412 (2022)